|
|
Topic: P301 |
High-Speed Output |
|
|
|
Topic: P301 |
High-Speed Output |
|
The following section discusses the configuration and options available with the High-Speed Output Module.
For applications that require coordinated axis control, consider the Productivity Advanced motion Control, PS-AMC, modules. The configuration of the PS-AMC modules is covered in the AMC Hardware Configuration topic.
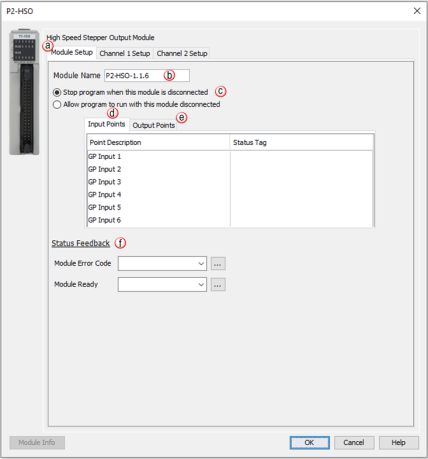
Note: The Input Points are not updated in STOP mode.
Registers: Enter a tag to view the count for each register within the Programmable Limit Switch (PLS) instruction (read-only).
Note: If an error message is present due to a fault, once the fault is corrected, a power cycle or a triggering of an SPOS instruction will clear the error.
|
Error Bit |
Error |
Description |
|
1 |
Missing External Power |
This module requires that external power be supplied in order to operate. If there is a loss of the supplied power, this bit will turn ON and all of the front panel fault LEDs will blink. |
|
2 |
Overload / Short Circuit Output 1 |
Each of the module outputs has built-in ESCP (Electronic Short Circuit Protection). This bit indicates a fault has occurred with Output 1. If a move was in progress, the Move Status Bit 12“Aborted-IO Fault”will be set for that particular move instruction. See the specific move instruction topic for the error bits associated with it. |
|
3 |
Overload / Short Circuit Output 2 |
Each of the module outputs has built-in ESCP (Electronic Short Circuit Protection). This bit indicates a fault has occurred with Output 2. If a move was in progress, the Move Status Bit 12“Aborted-IO Fault”will be set for that particular move instruction. See the specific move instruction topic for the error bits associated with it. |
|
4 |
Overload / Short Circuit Output 3 |
Each of the module outputs has built-in ESCP (Electronic Short Circuit Protection). This bit indicates a fault has occurred with Output 3. If a move was in progress, the Move Status Bit 12“Aborted-IO Fault”will be set for that particular move instruction. See the specific move instruction topic for the error bits associated with it. |
|
5 |
Overload / Short Circuit Output 4 |
Each of the module outputs has built-in ESCP (Electronic Short Circuit Protection). This bit indicates a fault has occurred with Output 4. If a move was in progress, the Move Status Bit 12“Aborted-IO Fault”will be set for that particular move instruction. See the specific move instruction topic for the error bits associated with it. |
|
6 |
Overload / Short Circuit Output 5 |
Each of the module outputs has built-in ESCP (Electronic Short Circuit Protection). This bit indicates a fault has occurred with Output 5. If a move was in progress, the Move Status Bit 12“Aborted-IO Fault”will be set for that particular move instruction. See the specific move instruction topic for the error bits associated with it. |
|
7 |
Overload / Short Circuit Output 6 |
Each of the module outputs has built-in ESCP (Electronic Short Circuit Protection). This bit indicates a fault has occurred with Output 6. If a move was in progress, the Move Status Bit 12“Aborted-IO Fault”will be set for that particular move instruction. See the specific move instruction topic for the error bits associated with it. |
|
8 |
Firmware Image CRC Error |
Module Firmware is faulted. |
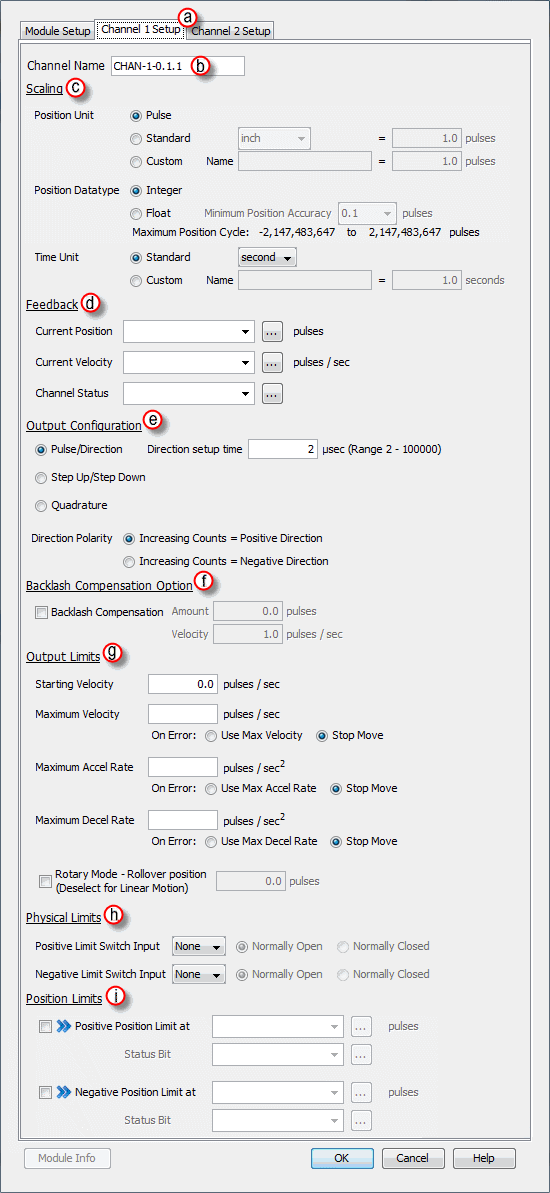
- Position Unit: Pulse: This option uses the raw Pulse per position unit selection.
- Position Unit: Standard: This option configures the numbers of pulses per unit. There are five pre-defined labels that can be selected: inch, foot, mm, degree and revolution. The pulses can also be specified in fractional increments (.1).
Once the scaling factor has been configured, the ladder logic can specify the target values to the HSO in the units that make sense for the application. For example: If a scaling value of 10 was configured and the ladder logic specified a target value of 10, the HSO would physically output 100 pulses.- Position Unit: Custom:This option also configures the number of pulses per unit but allows for a custom label to be entered. The pulses can also be specified in fractional increments (.1).
Once the scaling factor has been configured, the ladder logic can specify the target values to the HSO in the units that make sense for the application. For example: If a scaling value of 10 was configured and the ladder logic specified a target value of 10, the HSO would physically output 100 pulses.- Position Datatype: The position may be specified in terms of Integer or Float. Integer will provide a greater range but may be difficult to use when using the Scaling function. Conversely, Float will provide greater resolution in some cases but will greatly limit the range. The more resolution specified, the lower the range. It may be beneficial to scale the signal first then change the Position Datatype if needed to achieve the desired resolution and/or range. See the Understanding Maximum Position Cycle and Minimum Position Accuracy topic for more information.
- Time Unit: Standard: Choose the appropriate Time unit which will be used for this channel's time base. The three choices available are: second, minute and hour.
- Time Unit: Custom: A custom number of seconds can be configured in this field. The number of seconds can be entered in fractional increments (.1).
- Current Position Feedback: Insert a tag into this field in order to reference the channel’s current Pulse Count. The value will be represented in the scaled units specified from the Channel Scaling setup.
- Current Velocity Feedback: Insert a tag into this field in order to reference the channel’s current Velocity. The value will be represented in the scaled units specified from the Channel Scaling setup.
- Current Status: Insert a tag into this field in order to reference the current Status of the channel. A list of the possible Channel Status codes are listed below:
|
Status Bit |
Status |
Description |
|
1 |
Px-HSO Only:Last Direction Backlash Positive |
These bits indicate the last direction of travel. They are updated as soon as channel movement starts. If Backlash has been configured then these bits will not change state until after backlash has been “taken up” in the opposite direction. |
|
2 |
Px-HSO Only:Last Direction Backlash Negative |
|
|
3 |
Future |
Future |
|
4 |
Future |
Future |
|
5 |
Future |
Future |
|
6 |
Future |
Future |
|
7 |
Future |
Future |
|
8 |
Future |
Future |
|
9 |
Positive Limit Switch Tripped/p> |
These limit switches are configured and operate independently of each other. They are enabled individually allowing you to have just a positive, just a negative, or both limits. Each Limit Switch is only detected in its direction of travel. So an active Negative Limit will not prevent movement in the Positive Direction (and vice-versa). This allows a channel to “back off” of a Limit Switch in the opposite direction. But this also means that the Limit Switches will not protect from an axis traveling in the wrong direction. Note 1: If both Limit Switches are configured to the same Input then you will not be able to “back off” of the limit, manual interaction would be required, this type of setup is usually called “over-travel limit”. Note 2: The relevant instruction's Move Status Bit 10 “Aborted – Hit Limit” is also set at the same time. |
|
10 |
Negative Limit Switch Tripped |
|
|
11 |
Future |
Future |
|
12 |
Future |
Future |
|
13 |
Px-HSO Only:Positive Position Limit Tripped |
These bits indicate when the channel's current position violates the Position Limit setup in the H/W Configuration. Position Limits allow the axis movement to be restricted without physical limit switches. The Position Limits are configured and also operate independently of each other. They are enabled individually allowing you to have just a positive, just a negative, or both limits. Note 1:The relevant instruction's Move Status Bit 10 “Aborted – Hit Limit” is also set at the same time. Note 2: These limits can be changed on the fly during a move. Note 3: Position Limits are ignored during HOME instructions since the Home position of the Channel has not been matched to a physical Axis position. |
|
14 |
Px-HSO Only: Negative Position Limit Tripped |
|
|
15 |
Registration Stop Tripped |
When an instruction is configured for Registration and the Decel to a Stop option is selected, this bit will turn ON after the channel comes to a stop. Also the relevant instruction's Move Status Bit 8 “Stopped at Registration Target” will be set. |
|
16 |
Module Error - See Module Error Code (above) |
This bit indicates that an error exists in the Module Error Code, look there for further information. |
|
Status Bits 17-32 are used only by the PS-AMCx Modules |
||
|
17 |
Info- Encoder is a Master |
The encoder is an active Master of a drivetrain |
|
18 |
Info- Axis is a Master |
This axis (not the encoder) is an active Master of a drivetrain |
|
19 |
Info- Axis is a Slave |
This axis is an active Slave in a drivetrain |
|
20 |
Info- Axis is Enabled |
When configured with “Axis requires Enable”, this is HI when AEN is active |
|
21 |
Info- Position Deviation Exceeded |
If configured, this will be HI if the difference between the Encoder position and the commanded position is greater than the configured deviation window. |
|
22 |
Info- Capture Input Previously Defined |
MREG Only: The define position capture input/edge has already been defined for capture |
|
23 |
Future |
Future |
|
24 |
Aborted- Drive Not Ready |
When configured with “Axis Uses Drive Ready”, the target axis is not providing a ready state signal on IN1- Drv Rdy |
|
25 |
Aborted- Axis at Limit At Start |
Axis is on the limit sensor at the start of a move in that direction |
|
26 |
Aborted- Axis Not Enabled |
When configured with “Axis Requires Enable”, this is HI when the AEN instruction is not active and a move on this axis is trying to start or during the move |
|
27 |
Aborted- Position Deviation Stop |
When configured, the axis was stopped due to the difference between the Encoder position and the commanded being greater than the configured deviation window. |
|
28 |
Aborted- Axis is a Drivetrain Slave |
Axis cannot be used by another instruction because it is an active Slave to another Master axis. |
|
29 |
Aborted- Axis is Linear |
Axis is configured as a Linear axis when it is required to be Rotary Axis |
|
30 |
Aborted- Slave Exceeded Maximum Velocity |
Axis is an active Slave and was commanded to go faster than maximum allowable configured velocity of the axis. This usually is because the gear ratio is too high |
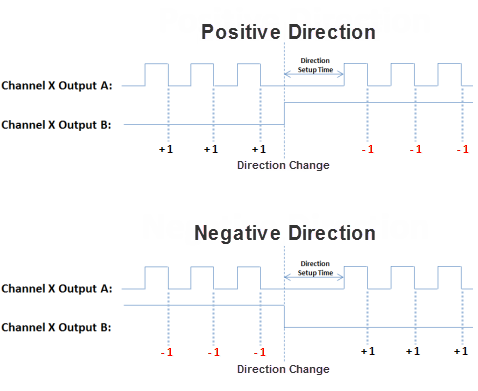
- Pulse/Direction: This selection configures the module to generate the Pulse Train on Output A of the channel and the Direction is established on Output B of the channel. When the logic tells the module to change direction, Output B will toggle from low to high and vice versa. The Direction Setup Time field specifies how long the direction signal should be established before the pulse train starts. The range is from 2 microseconds to 100 milliseconds. If the module is currently sending a pulse train and a direction change has been issued, the module will freeze the pulse outputs for the time period specified.
- Step Up/Step Down: When this option is selected, the Pulse Train is generated on Output A when a Positive direction has been specified and on Output B when a Negative direction has been specified.
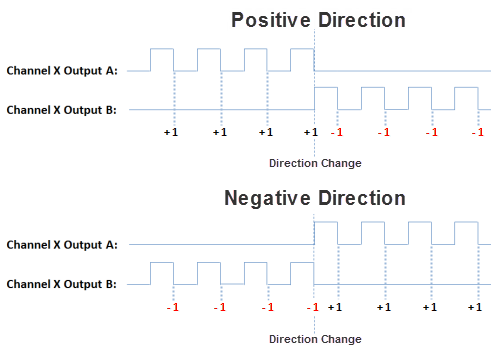
- Quadrature: When this option is selected, the Pulse Train output is generated on Output A and Output B, offset by a 1/2 cycle. Direction changes from the logic cause the offset to change from one output to the other. There are also Direction Polarity options that allow the polarity to be changed logically.
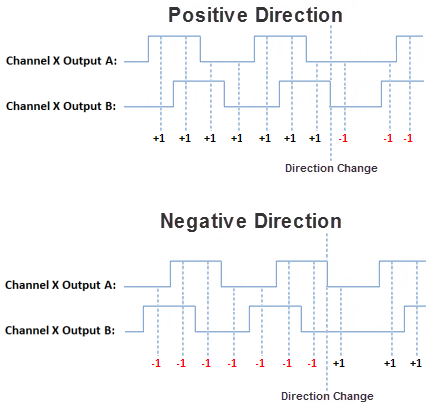
- Direction Polarity: The Direction Polarity setting determines the initial sequence of the Pulse offsets or Direction Line level. Refer to the Pulse Train Output Configuration diagrams above to see how this setting affects the initial Pulse output sequence.
- Starting Velocity (Pulses/sec): The velocity to start at when accelerating to higher target velocities. This is typically set to the maximum rate the motor can instantaneously achieve from a stopped state. The system must be able to withstand the jerk created by this immediate velocity change. Using this feature can reduce acceleration/deceleration times, and therefore reduce process cycle times. For target velocities below the Starting Velocity, there is no acceleration/deceleration, and the profile will start and stop at the target rate without ramping.
- Maximum Velocity (Pulses/sec): This is the maximum Pulse rate that the module will output. The On Error selections specify how the module should behave when the maximum rate is exceeded. The module can be configured to maintain the maximum rate or to Stop the move if a pulse rate higher than the maximum is specified by the logic.
- Maximum Accel Rate (Pulses/sec2): This is the maximum Acceleration rate that the module will output. The On Error selections specify how the module should behave when the maximum rate is exceeded. The module can be configured to maintain the maximum rate or to Stop the move if an acceleration rate higher than the maximum is specified by the logic.
- Maximum Decel Rate (Pulses/sec2): This is the maximum Deceleration rate that the module will output. The On Error selections specify how the module should behave when the maximum rate is exceeded. The module can be configured to maintain the maximum rate or to Stop the move if a deceleration rate higher than the maximum is specified by the logic.
- Rotary Mode - Rollover Position: If selected, when the count reaches the specified rollover position, the next positive pulse will reset the count to 0. Also, if the count is at 0, the next negative pulse will reset the count (roll under) to the specified rollover position. The value is specified in user units but the final scaled value must be within 1 and 2,147,483,647 whole counts. If the final scaled roll over position value is not a multiple of whole pulses, the fractional pulse amount will be ignored. When this feature is used, the count will always be a positive number between 0 and the rollover position.
- Positive Limit Switch Input: This option will stop the module pulse output if the specified Limit Switch becomes true when encountered in the Positive direction. An error will be indicated in the Module Error Code tag when this occurs. Motion in the negative direction is permitted in this state to allow for movement away from the limit switch unless the same switch is used for both positive and negative limits.
- Negative Limit Switch Input: This option will stop the module pulse output if the specified Limit Switch becomes true when encountered in the Negative direction. An error will be indicated in the Module Error Code tag when this occurs. Motion in the positive direction is permitted in this state to allow for movement away from the limit switch unless the same switch is used for both positive and negative limits.
- Enable Positive Position Limit at: This option will stop the module pulse output (unless performing a Homing routine) if the module reaches the count specified (constant or Tag value) while traveling in the Positive direction. An error will be indicated in the Status Bit specified when this occurs. As with the hardware switch limits, movement is allowed in the negative direction in order to move away from the limit switch. The "On the fly" symbol
indicates that this value can be changed while the instruction is running.
- Enable Negative Position Limit at: This option will stop the module pulse output (unless performing a Homing routine) if the module reaches the count specified (constant or Tag value) while traveling in the Negative direction. An error will be indicated in the Status Bit specified when this occurs. As with the hardware switch limits, movement is allowed in the positive direction in order to move away from the limit switch. The "On the fly" symbol
indicates that this value can be changed while the instruction is running.