Description
The
P3-530
CPU
is configured using the setup tools found in the
Hardware Configuration
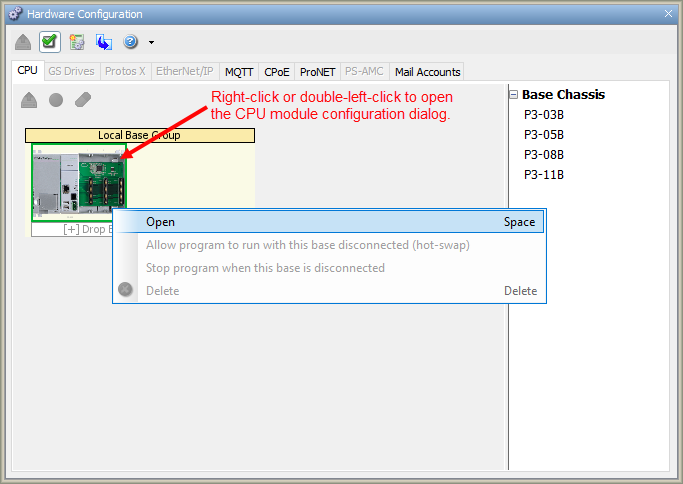
window. First select the
Local Base Group
from the
Hardware Configuration
window by double left-clicking the
Local Base Group or by
right-clicking the
Local Base Group and
selecting Open from the drop
down menu as seen below.
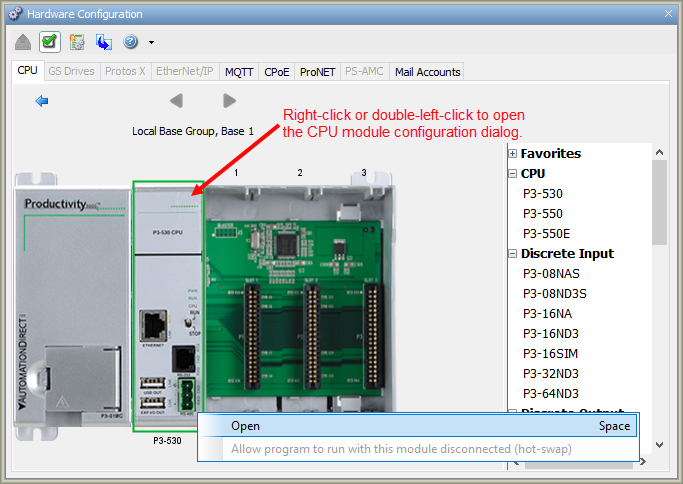
Then select the
P3-530 by double
left-clicking the CPU or by
right-clicking the CPU and
selecting Open from the drop
down list. This will display the
P3-530 configuration window.
Options Tab Configuration
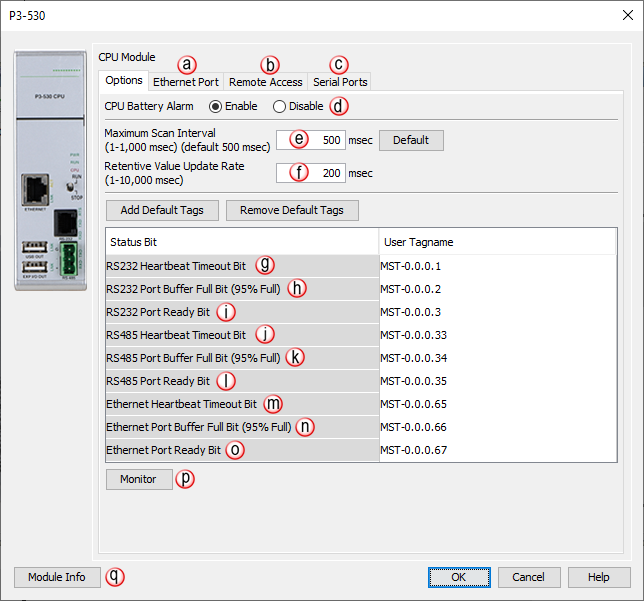
- Ethernet Ports Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Ethernet Ports Configuration
dialog.
- Remote Access Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Remote Access Configuration
dialog.
- Serial Ports Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Serial Ports Configuration
dialog.
- CPU Battery Alarm (Enable/Disable):Enables or
Disables the
Low Battery Voltage Alarm.
- Maximum Scan Interval:
Sets the value for a
Watchdog Timer
that will trigger a
Maximum Scan Interval Internal
tag if the
Preset Time is
exceeded.
- Retentive Value Update Rate:
User defined
Tags that are
set as
Retentive will
be Saved at the
Periodic Rate
specified here.
- RS-232 Heartbeat Timeout Bit:
Allows the ladder logic in the
CPU to know if a
device has stopped communicating to the
CPU. The
RS-232 Heartbeat Timeout Bit
will become true if the
RS-232 Comm Heartbeat Value
of the
Serial Ports
configuration is exceeded, but only when the CPU ports are
being used as a slave device. The CPU monitors the time between
communications from the master device and enables the Bit if a
communication packet fails to be received by the CPU within the
specified time.
- RS-232 Port Buffer Full Bit (95% Full):
A
Boolean Tag can
be assigned to this field and then used in the ladder code to indicate
when communications are almost maxed out on this
Port. When
the Port becomes
95% full, the
Bit becomes true
(value of 1).
- RS232 Port Ready Bit:
Indicates when the
RS-232 Port is ready to be
used for communications to other devices.
RS-232 Port Ready Bit will
become momentarily false during a stop mode transfer of the programing
software.
- RS-485 Heartbeat Timeout Bit:
Allows the ladder logic in the
CPU to know if a
device has stopped communicating to the
CPU. The
RS-485 Heartbeat Timeout Bit
will become
True if the
RS-485 Comm Heartbeat Value
of the
Serial Ports
configuration is exceeded, but only when the CPU ports are
being used as a slave device. The CPU monitors the time between
the communications from the master device and enables the
Bit if a communication packet fails to be received by the
CPU within the specified time.
- RS-485 Port Buffer Full Bit (95%):
A
Boolean Tag can
be assigned to this field and then used in the ladder code to indicate
when communications are almost maxed out on this
Port. When
the Port becomes
95% full, the
Bit becomes
True (value of
1).
- RS485 Port Ready Bit:
Indicates when the
RS-485 Port is ready to be
used for communications to other devices.
RS-485 Port Ready Bit will
become momentarily false during a stop mode transfer of the programing
software.
- Ethernet Heartbeat Timeout Bit:
Becomes True if the Ethernet Comm Heartbeat Value of the
Ethernet Ports configuration is exceeded, but only when the
CPU ports are being used as a slave device. The
CPU monitors the time between the communications from the
master device and enables the Bit if a communication packet fails to
be received by the CPU within the specified time.
- Ethernet Port Buffer Full Bit (95% Full):
Becomes True if the
External Ethernet Port Buffer is 95% full. A
Boolean Tag can be assigned to this field and used in the
ladder code to indicate when communications are almost maxed out on
this Port. Instructions which use the
Port Buffer Output Queues: MRX/MWX, RX/WX, GSR/GSW, DWX, AOUT,
CPO.
Note:MST bits correlating to
any
Buffer Full Bit (95% Full)
correspond to the queue of instruction data that was executed but is
still waiting to be transmitted out of a port. Each Serial port can
buffer 100 instructions,
and the local Ethernet port can buffer
1000 instructions. The
95% Bit is not related to
the number of bytes waiting, but instead to the number of instructions
that have data waiting.
USB Out Port
- Ethernet Port Ready Bit: Indicates when the
Ethernet Port is ready to be used for communications to other
devices. Ethernet Port Ready Bit will become momentarily
False during a stop mode
transfer of the programing software.
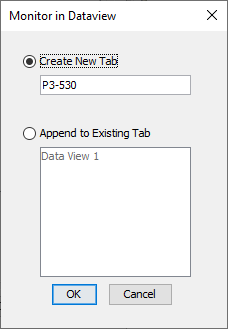
- Monitor: Displays the window shown below with options for
adding tags to
Data View.
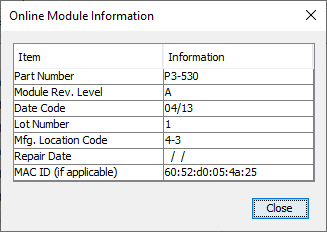
- Module Info: Click on this button to open a window that
displays information about the specific Module. A sample of
theOnline Module Informationis shown below.
Ethernet Ports
Configuration
- Options Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Options
dialog.
- Remote Access Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Remote Access Configuration
dialog.
- Serial Ports Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Serial Ports Configuration
dialog.
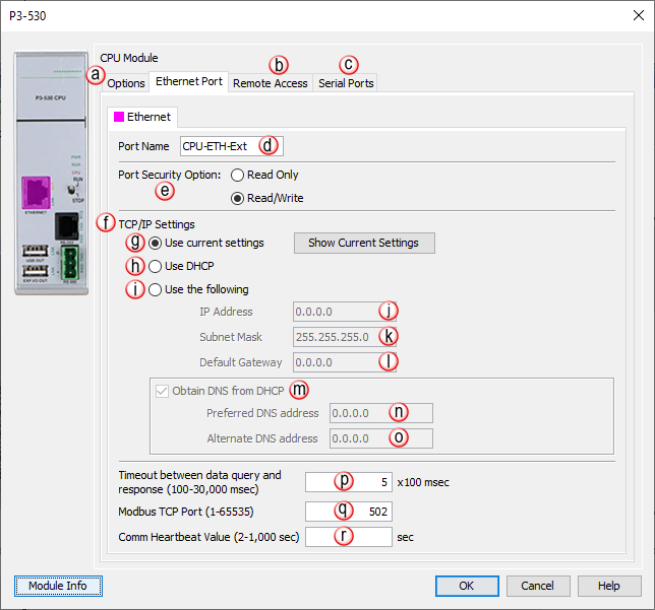
- Port Name:
Allows the entry of a unique
Name for the
External Ethernet Port. This Name is
referenced in the
Communications
instructions (MRX, MWX,
RX,
WX).
- Port Security Option:
Can be used as a simple
Security measure
to prevent
Modbus RTU write
requests from being accepted by the
CPU. To
allow Reads and
Writes, select
Read/Write.
- TCP/IP Settings: TheIP Setting of
thisPortmay be changed in several ways:
-
The
Settings may
be entered manually in the
Choose CPU
tool. This allows the user to make changes to the
IP to allow
connection by the computer running the
Productivity Programming Software. Changes are sent using
Multicast Messages.
-
The
Settings can
be saved as part of the project. This must be
Enabled in the
P3-530 Hardware Configuration Settings
by selecting
Use the Following
(discussed on
Item k below).
If handled this way, the
Settings
stored in the project will take effect at
Project Transfer
and at boot up only. The
Settings may
be changed after boot up.
- Use Current Settings:
When selected,
Project Transfer
or boot up will not make changes to the
TCP/IP Settings
of the CPU.
- Use DHCP: This
specifies that the
CPU should
request its
IP Settings from
a DHCP Server on
the network.
Note: If the CPU
is set to use DHCP for its IP Settings it cannot, in all likelihood,
be used as a Modbus TCP Server since most industrial Modbus TCP Clients are targeting a fixed IP address. If the CPU is set to DHCP, its IP address may change on any given day and the Modbus TCP client will not be able to target it.
Note: Selecting
Show Current Settings and
DHCP= No, this indicates
the CPU could not find an
available DHCP server. A
default address of
10.10.10.10 will be
assigned if no available server is found.
Note: Only after a power
cycle will the CPU begin
to search for an available
DHCP server.
- Use The Following:
If this
Option is
selected, the
CPU will set
itself to the specified project
Settings upon
Project Transfer
or at boot up.
- IP Address: This
field is where the
IP Address is
specified in
Four Octets.
For Example: 192.168.1.5
Note:
Entering an IP Address reserved for specific functions will cause an error dialog box to be displayed upon project compile.
- IP address cannot begin with 127
-
The bits of the network or host portion of an IP address cannot be
all 0's or all 1's. For example, 192.168.170.0 with network mask of
255.255.254.0 is invalid since the bits of the host portion of the
address are all 0's.
-
IP address must between 1.0.0.1 and 223.255.255.254 (Excluding
10.20.x.x used for Local (Remote I/O) network. All Productivity CPUs
except P3-530 and P1-540).
Note: This address range
is restricted for only Remote I/O supported by a Productivity CPU.
- Subnet Mask:
Specified in four octets (i.e., 255.255.255.0) and used in conjunction
with the IP Address to configure a
Logical Network.
- Default Gateway:
This field is where the
Default Gateway Address
is specified in
Four Octets
(i.e.,
192.168.1.1).
This is typically the
IP Address of
the router on the network. If a target
IP Address is
specified in an outgoing message from the
CPU that is not
in the
Local Subnet,
the
Default Gateway Address
is where this message will be sent.
-
A
DNS (Domain Name Service)
server contains a database of public IP addresses and their
associated host names and translates those common names to
IP addresses. For example, a DNS server translates
“www.automationdirect.com” to the IP address 205.151.114.26. A
Preferred and Alternate DNS address can be configured for
redundancy.
Note: Other names for a DNS server include name
server, nameserver, and domain name system server.
- Preferred DNS Server IP Address: the IP Address of the first DNS server to
contact for resolving the Name to an IP Address.
- Alternate DNS Server IP Address:the IP Address of an alternate DNS server to
contact if the preferred DNS server cannot resolve the
Name to an IP Address.
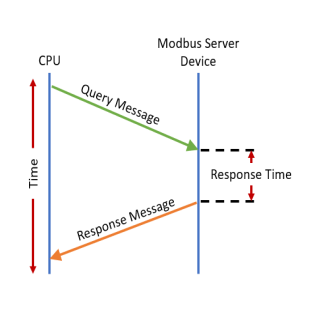
- Timeout Between Data Query and Response:
The Time period
between the queries sent from the
CPU (via a
Communication
instruction, such as a
MRX,
MWX,
RX or
WX) and the
Time a response
from that device is received. If the
Response takes
longer to receive (or is not received) than the specified
Time period, a
Timeout Error
will occur for the given instruction. Each instruction has a
Timeout Status
bit that can be assigned to it. See the diagram shown below.
- Modbus TCP Port:
The listening
TCP Port Number
for
Modbus TCP
connections. If necessary, this value can be adjusted for
advanced router access. In most situations, this
Number should be
left at 502.
- Comm Heartbeat Value:
If a communication packet fails to be received by the
CPU within the specified time-period, the
System Bit Ethernet Heartbeat Timeout Bit will become true. If
a value is placed in this field, the CPU will start a timer
between each communication packet coming into the CPU. This
feature allows the ladder logic in the CPU to know if a device
has stopped communicating to the CPU.
Remote Access
Configuration
- Options Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Options
dialog.
- Ethernet Ports Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Ethernet Ports Configuration
dialog.
- Serial Ports Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Serial Ports Configuration
dialog.
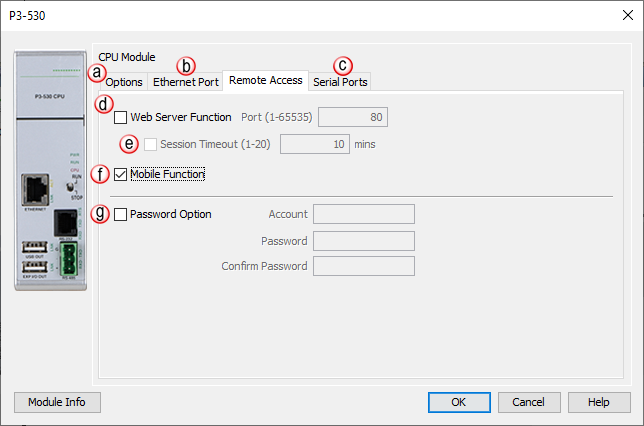
- Web Server Function:
Provides the means to make a non secure web connection to the
CPU in order to access the
USB pen drive and view
read-only system tags. When enabled, a port number selection is
required.
-
Port: (Default 80) Allows user to set a port number ranging from
1-65535.
-
Session Timeout: Allows
the user to set a specific time limit (1-20 mins.) on inactivity
that will close the
Web Server
connection. If there is no activity between the
PC and the
Web Server
for the specified time limit, the connection will close.
- Mobile Function: Enables
Remote Access which allows
the
CPU Data Remote Monitor App
to monitor the selected tags.
-
Password Option: Allows
the user to set a password for Remote Access using the
CPU Data App or access
to the
Web Server.
-
Enter an account name & password of up to a combination of 20
numbers and characters (can include special characters).
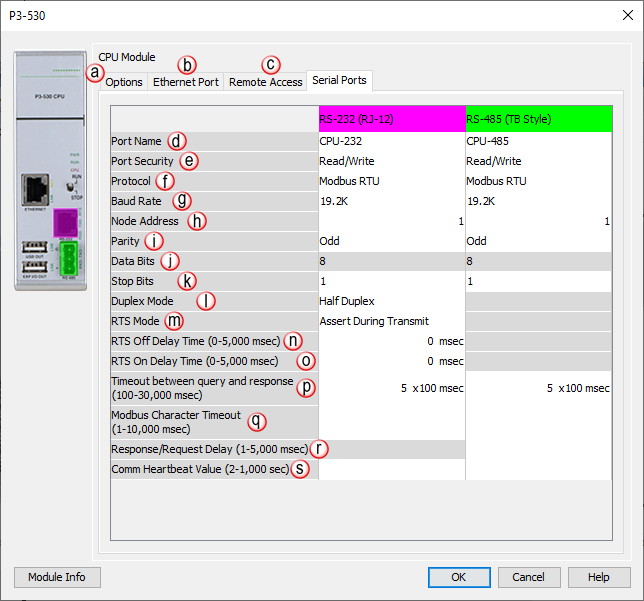
Serial Ports Configuration
There are two
Serial Ports on
the P3-530 . There
is an
RS-232 Port with
an RJ-12 connector
and a
2-wire RS-485 Port
with a removable three-pin terminal block. Both
Ports are capable
of
Modbus RTU Client
(device that initiates communications requests) and
Server (device
that responds to communications requests) communications. They are
also capable of
ASCII outgoing
strings and incoming strings.
When the Serial Ports Tab is selected, the
Serial Ports settings are displayed as shown below.
- Options Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Options
dialog.
- Ethernet Ports Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Ethernet Ports Configuration
dialog.
- Remote Access Tab:
Click on this
Tab to go to the
Remote Access Configuration
dialog.
- Port Name:
Allows the entry of a unique
Name for the
RS-232 and
RS-485 Ports.
This name is referenced inside of the
Communications
instructions (MRX, MWX,
RX,
WX) and
ASCII
instructions (AIN, AOUT,
CPO,
CPI) to select
the Port to send
or receive the request.
- Port Security: Can be used as a simpleSecurity
measure to preventModbus RTU write requests from
being accepted by the CPU. To allow
Readsand Writes, select Read/Write.
- Protocol:
Determines whether the
Port is used for
Modbus RTU
communications, sending or receiving
ASCII Strings or
performing the
Custom Protocol
function.
- Baud Rate:
Choose from a drop-down list of available
Baud Rates (1200, 2400, 9600, 19200, 33600, 38400, 57600, and
115000). All devices communicating on the network must be set to the same
Baud Rate.
- Node Address:
This field can be set from 1 to 247 and is used to uniquely identify
the CPU on the network, only when the CPU is a
Modbus RTU Server device. This setting is sometimes referred to
as a Station Address
- Parity: Used for
simple, low-level Error Detection. All devices on the network must be
at the same Parity setting. Valid selections are None, Even, and Odd.
- Data Bits:
Determines whether the communications packet uses
Seven Data Bits
or
Eight Data Bits.
Eight Data Bits
is the only valid selection for
Modbus RTU.
Either
Seven or
Eight Data Bits
can be selected when using
ASCII
communications. Set this field to match the device that is
connected to the
CPU.
- Stop Bits:
Determines whether the communications packet uses
One or
Two Stop Bits.
Set this field to match the device that is connected to the
CPU.
- Duplex Mode: In
ASCII/Custom Protocol mode, Half Duplex or Full Duplex can be chosen.
- Half Duplex: When selected, the Serial Port can either
transmit or receive, but not both at the same time.
- Full Duplex: When selected, allows the Serial Port to
transmit and receive simultaneously (Only available in ASCII/Custom
Protocol).

- RTS Mode: Set
the RTS mode to control
the Request To
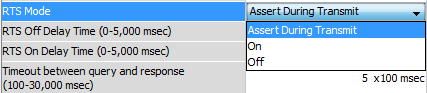
Assert During Transit: Make the RTS signal
turn ON in the time between
the RTS ON delay and
RTS OFF delay (only
available in
Half Duplex Mode).
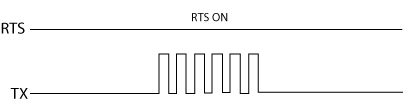
ON: Make the RTS signal ON all the time.
OFF: Make the
RTS signal
OFF all the time.
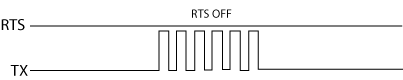
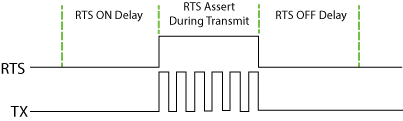
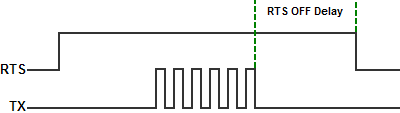
- RTS OFF Delay Time (RS-232 Only):
The amount of Time between the end of the data transmission to
when the RTS signal is turned off. The diagram below
illustrates this. This setting may be needed when using media
converters (RS-232 to RS-422/485 converters) and/or radio
modems. A delay may be needed at the end of the data transmission for
processing time in the device.
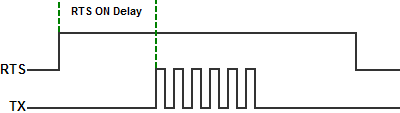
- RTS On Delay Time (RS-232 Only):
The amount of Time between when the
RTS Signal is turned
ON and the data
transmission begins. The diagram below illustrates this. This setting
may be needed when using media converters (RS-232 to RS-485
converters) and/or radio modems. A delay may be needed after the
assertion of the RTS Signal and when the data transmission begins for
processing time in the device.
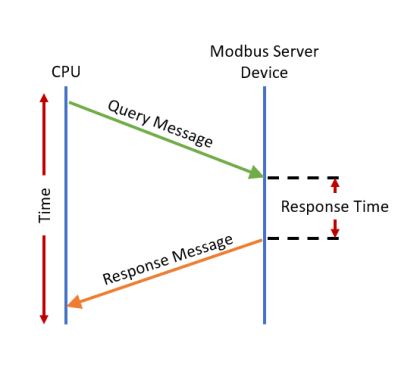
- Timeout Between Query and Response:
The allowable Time between when a query is sent from the
CPU (via a Communication instruction, such as an
MRX, MWX, RX, or WX) and when a Response from that
device is Received, before a Timeout Error will occur
for the given instruction. Each instruction has a
Timeout Status bit that can be assigned to it.
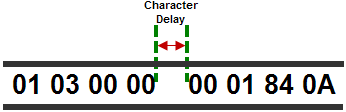
- Modbus Character Timeout:
The Time between
two bytes (or characters) within a given
Modbus Message.
The
Modbus RTU
specification states that this time must be no more than
1.5 Character Times
(real time based on
Baud Rate).
Sometimes delays do occur between bytes when using radio modems,
media converters, etc. This setting allows some tolerance in
these situations for the incoming
Modbus Messages
in the CPU.
The CPU
will wait for the amount of time specified in this field before
discarding the incomplete packet. If the
CPU does not
receive the remainder of the
Message within
the specified
TimeFrame, it will
discard the first portion of the
Message and wait
for a new
Message.
- Response/Request Delay (RS-485 Only):
Used when the
CPU is a
Modbus RTU Server
or Client on the
RS-485 Port.
The total
Response Time can
be up to the
Total CPU Scan Time +
the
Value specified in
this field. When using
2-wire RS-485
communications, sometimes
Echoes can occur
since both devices use the same differential signal pair to send and
receive.
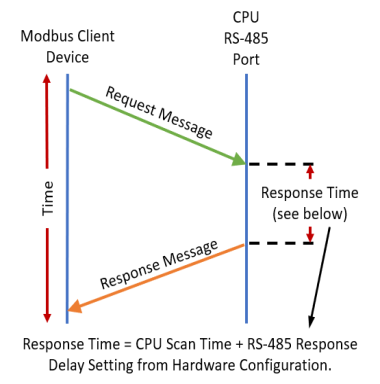
-
If acting as a Server,
upon receiving a
Modbus Request, the CPU
will wait for the time period specified in this field before sending
a Response. This can be
used with slow clients that need extra time to change from sending
to receiving.
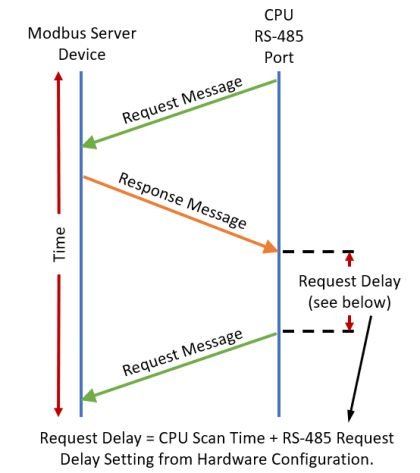
-
If acting as a Client,
after receiving a
Modbus Response, the CPU
will wait for the time period specified in this field before sending
another Request. This
can be used to delay request messages in order to give extra time
for slow server devices.
- Comm Heartbeat Value:
If a value is placed in this field, the CPU will set the
System Bit RS-232 Heartbeat Timeout Bit or RS-485 Heartbeat Timeout
Bit to True, if a communication packet fails to be received by the
CPU within the specified Time period. This feature
allows the ladder logic in the CPU to know if a device has
stopped communicating to the CPU.


















