Topic: CL222
| High Speed Count |
Topic: CL222
|
High Speed Count operates independently of the CPU program scan. Up to 6 Single-Input Counters or 3 Dual-Input Counters can be configured.
![]()
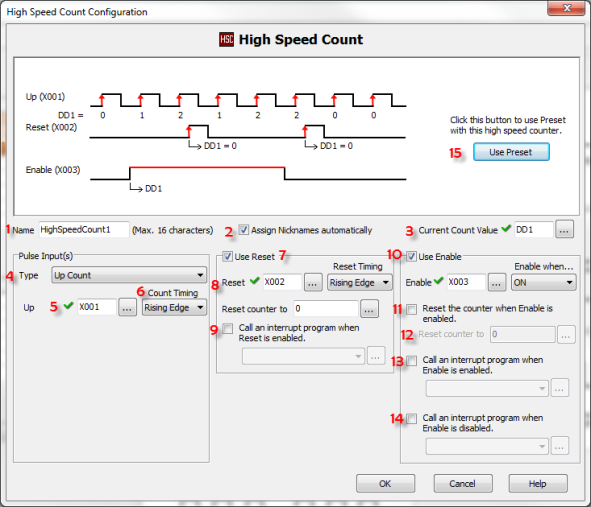
1 Name: This text is used to Prefix Nicknames of addresses used by this configuration..
2 Assign Nicknames automatically: Nicknames can be assigned to each address automatically. If you want to manage the Nicknames manually then disable this feature.
3 Current Count Value: This is the Accumulator register of the High Speed Counter.
4 Pulse Input(s) Type: There are six types available; Up, Down, Up/Down, Pulse/Direction, Quadrature, and Quadrature with Reset. The timing diagram displayed in the instruction updates to show the selected operation.
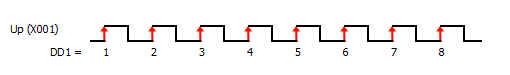
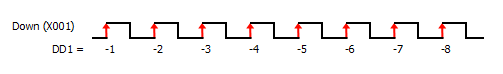
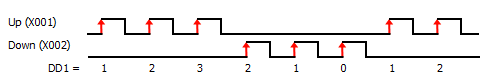
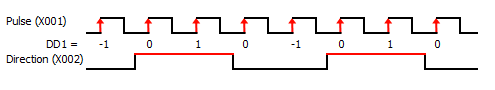
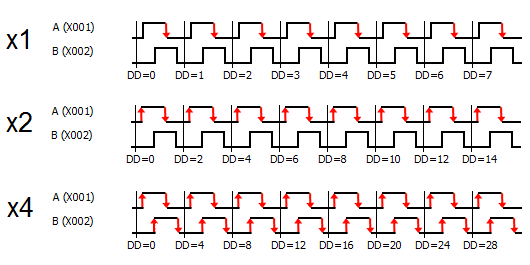
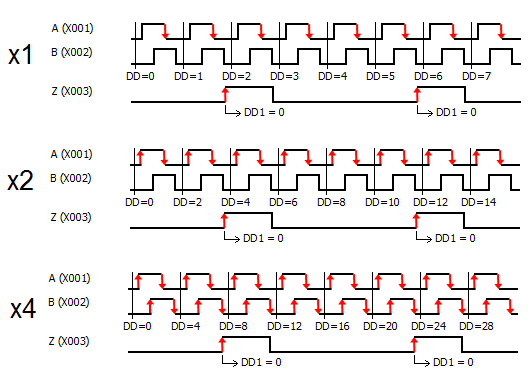
5 Pulse Input Bit: You can use only the CPU Built-in discrete inputs which are designated for high speed. Inputs cannot be shared by different high speed functions.
6 Count Timing: For each Pulse Input Type there will be different timing edge options.
7 Use Reset: Any X or C bit can be used to Reset the Counter on either the Rising or Falling Edge. If the counter has a Preset Table, this will also Reset the Current Preset Number to 1.
8 Reset:Use either a Constant or DD Memory Address which will be moved into the Current Count Value.
9 Call an interrupt program when Reset is enabled: An Interrupt Program can be called when the Reset operation is triggered. This option is grayed out if the Reset Input is not a high-speed Input
10 Use Enable: Any X or C bit can be used to Enable the Counter when either high or low. The Current Count Value is held while disabled.
11 Reset the counter when Enable is enabled: Optionally, set the Current Count Value to another value when the counter is Enabled. This will not cause a Preset Table Reset, only the Current Count Value is changed.
12 Reset counter to: Use either a Constant or DD Memory Address which will be moved into the Current Count Value.
13 Call an interrupt program when Enable is enabled: An Interrupt Program can be called when the Enable operation is triggered. This option is greyed out if the Enable Input is not a high-speed Input.
14 Call an interrupt program when Enable is disabled: An Interrupt Program can be called when the Disable operation is triggered. This option is greyed out if the Enable Input is not a high-speed Input.
15 Use Preset: Define a table of positions and actions to execute when the Current Count matches each preset. The purpose of the presets is to quickly cause an action upon arrival at specific counts. See Preset Table.
CPU Built-in
I/O Setup: Output Tab (Basic and Standard CPU)
CPU Built-in I/O Setup: General Tab (Basic and Standard CPU)
Example: Making the Preset Table Values Retentive