Topic: CL164
| Compare Contact |
Topic: CL164
|
The Compare A with B instruction uses a Mathematical Operator as a basis of comparison of two data values. A mathematical statement is developed using the instruction dialog. When the Data A and Data B values satisfy the selected mathematical relationship, the Compare Contact turns ON.
The fields Data A and Data B can contain memory addresses or Constants. Constants are created by typing the value directly into the Data A or Data B fields. Use the typing guidelines for the Data Type you are selecting. See the available Data combination to determine if two data types can be compared.
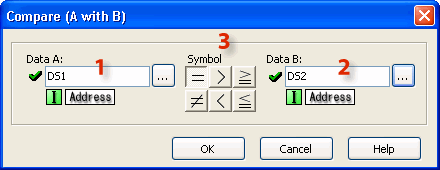
![]()
1 Data A: Select the first Data Memory Address or the Constant to be compared. The Data Memory Address or the Constant can be typed directly into the Address field on the dialog or the Data Memory Address can be selected from the Address Picker.
Click on the Browse Button![]() to open the Address Picker.
to open the Address Picker.
2 Data B: Select the second Data Memory Address or the Constant to be compared.
3 Symbol: Select the Mathematical Operator that defines the intended relationship between Data A and Data B.
Example Program 1: Compare Integer Data
In the following example, when DS1 is 100, Y001 will energize.

Example Program 2: Compare floating point data
In the following example, when DF1 is more than 2, Y001 will energize. As you can see, you can compare floating point data with integer or floating point data.

Example Program 3: Compare Hex data
In the following example, when XD1 is less than 200h, Y001 will energize.

Example Program 4: Compare Text data
In the following example, when TXT1 to TXT3 are ”ADC” (TXT1 = ”A”, TXT2 = ”D”, TXT3 = ”C”), Y001 will energize.
